In the ever-evolving world of technology, businesses and individuals rely on computing power to process data efficiently. Two dominant paradigms have emerged: cloud computing and edge computing. While both approaches aim to improve data processing and management, they differ significantly in terms of architecture, performance, and use cases.
This article explores the key differences between cloud computing and edge computing, helping you determine which is best suited for your needs.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services over the internet, including storage, processing power, and networking. These services are provided by third-party vendors such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Key Features of Cloud Computing:
- Centralized processing: All computations and data storage happen in remote data centers.
- Scalability: Cloud platforms allow businesses to scale resources up or down as needed.
- Cost efficiency: Pay-as-you-go models eliminate the need for expensive on-premise infrastructure.
- Remote accessibility: Users can access cloud services from anywhere with an internet connection.
Common Use Cases of Cloud Computing:
- Hosting websites and applications
- Big data analytics
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) processing
- Cloud storage and backup solutions
What is Edge Computing?
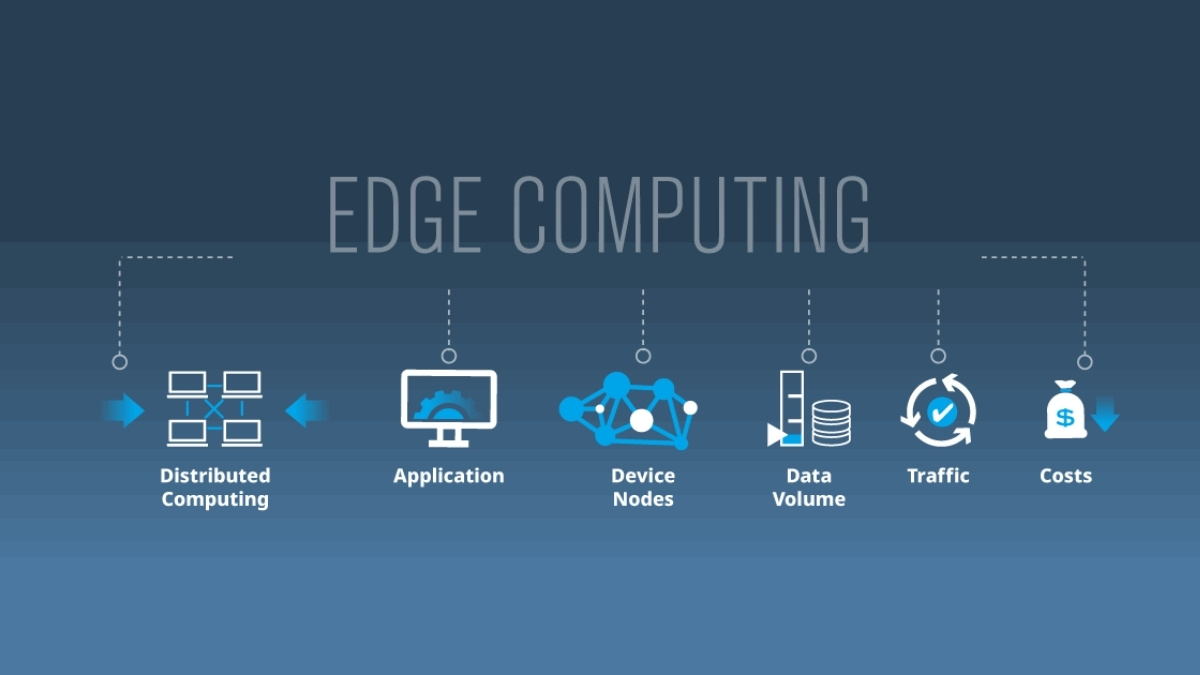
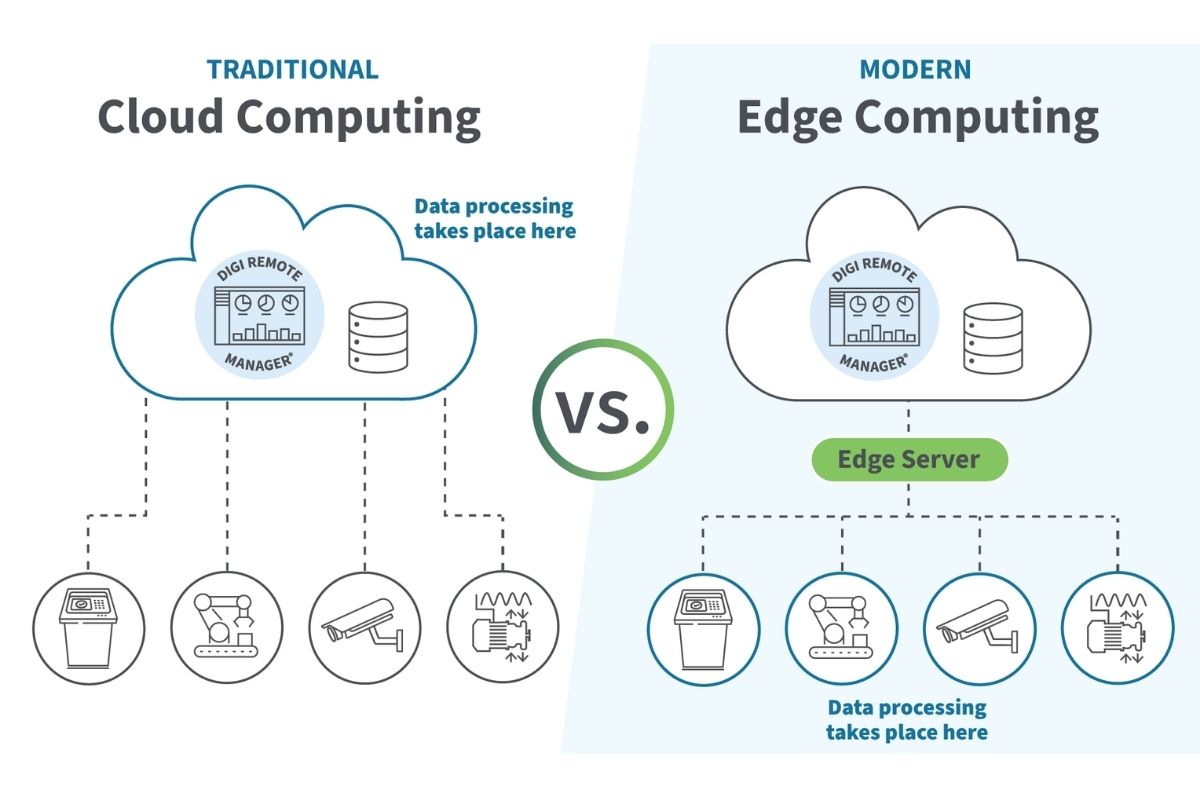
Edge computing is a decentralized computing framework where data is processed closer to its source rather than relying on centralized cloud servers. This reduces latency and enhances real-time processing capabilities.
Key Features of Edge Computing:
- Decentralized processing: Data is handled at the “edge” of the network, near the data source.
- Low latency: Reduces the time required to process data, making it ideal for real-time applications.
- Bandwidth efficiency: Limits the need to transmit large volumes of data to cloud servers, reducing bandwidth costs.
- Enhanced security: Sensitive data is processed locally, minimizing exposure to cyber threats.
Common Use Cases of Edge Computing:
- Internet of Things (IoT) applications
- Autonomous vehicles
- Smart cities and industrial automation
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) applications
Key Differences Between Cloud and Edge Computing
| Feature | Cloud Computing | Edge Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Location | Remote data centers | Near the data source |
| Latency | Higher due to distance | Lower due to local processing |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Limited by edge device capabilities |
| Bandwidth Usage | High | Lower, as data is processed locally |
| Security | Vulnerable due to centralized storage | Enhanced due to localized processing |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for large-scale operations | Can be costly due to hardware maintenance |
Choosing Between Cloud and Edge Computing
When to Use Cloud Computing:
- When you need scalable resources for large-scale applications.
- If data security and compliance require centralized storage and management.
- When real-time processing is not a priority.
When to Use Edge Computing:
- When low latency is critical, such as in autonomous driving or industrial automation.
- If you operate in remote locations with limited internet connectivity.
- When reducing bandwidth costs is a priority.
Conclusion
Cloud computing and edge computing each offer unique advantages, depending on specific use cases and operational needs. Cloud computing provides scalability, cost-efficiency, and remote accessibility, making it ideal for enterprises and data-heavy applications. Meanwhile, edge computing focuses on low latency, real-time processing, and enhanced security, making it suitable for IoT and mission-critical applications.
Understanding their differences enables businesses and individuals to make informed decisions about which approach to adopt. In some cases, a hybrid approach combining both cloud and edge computing can offer the best of both worlds.
Do you use cloud or edge computing in your business? Let us know in the comments below!