Medical emergencies can happen at any time, and knowing how to respond quickly and effectively can save lives. First aid is the initial assistance given to someone suffering from an injury or sudden illness before professional medical help arrives. This guide provides essential first aid tips for handling common medical emergencies.
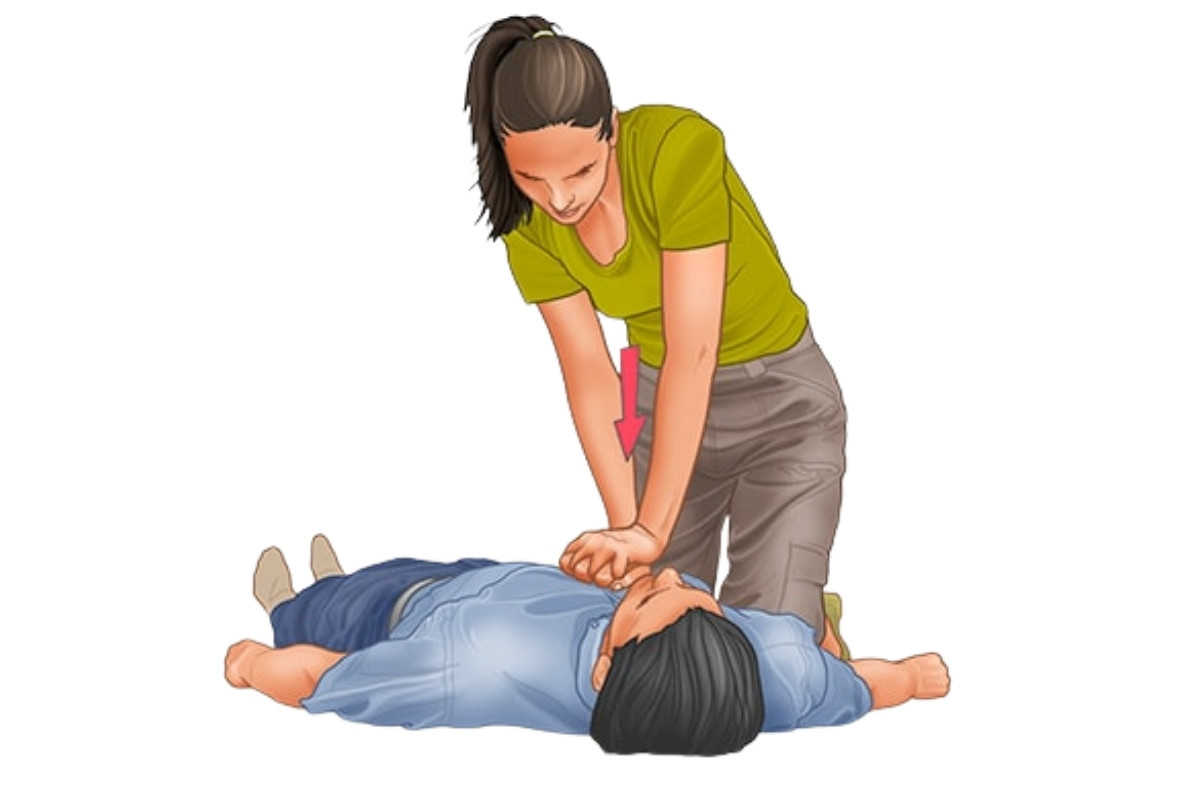
1. Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
CPR is a life-saving technique used when someone’s breathing or heartbeat has stopped.
Steps:
- Check responsiveness – Tap the person and shout to see if they respond.
- Call emergency services – Dial 911 or the local emergency number.
- Start chest compressions – Place hands on the center of the chest and push hard and fast (about 100-120 compressions per minute).
- Give rescue breaths – If trained, provide two rescue breaths after every 30 compressions.
- Continue until help arrives – Keep performing CPR until medical professionals take over.
2. Treating Severe Bleeding
Heavy bleeding can lead to shock and requires immediate attention.
Steps:
- Apply direct pressure – Use a clean cloth or bandage to press firmly on the wound.
- Elevate the injured area – If possible, raise the wounded limb above heart level.
- Apply a tourniquet (if necessary) – If bleeding is uncontrollable, use a tourniquet above the injury.
- Monitor for signs of shock – Keep the person calm and warm while waiting for medical help.
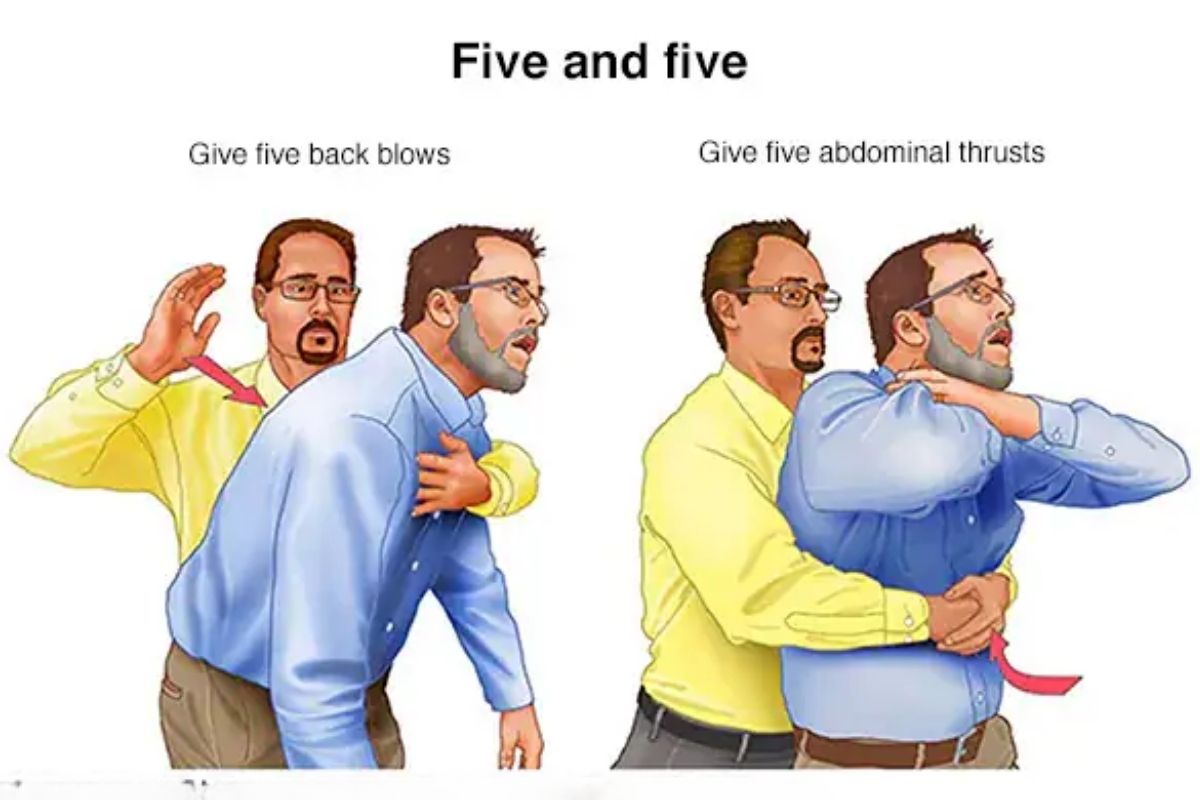
3. Managing Choking
Choking occurs when an object blocks the airway, preventing normal breathing.
Steps:
- Encourage coughing – If the person is conscious and coughing, let them try to clear the blockage.
- Perform the Heimlich maneuver – Stand behind the person, place a fist above their navel, and give quick inward and upward thrusts.
- Check the airway – If the object is visible, attempt to remove it carefully.
- Perform CPR if needed – If the person becomes unresponsive, start CPR immediately.
4. Handling Burns
Burns can be caused by heat, chemicals, electricity, or radiation.
Steps:
- Cool the burn – Run cool water over the burn for at least 10 minutes.
- Cover with a sterile dressing – Use a clean, non-stick bandage or cloth.
- Avoid breaking blisters – This can increase the risk of infection.
- Seek medical attention – For severe burns, call emergency services immediately.
5. Recognizing and Treating a Heart Attack
A heart attack occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked.
Symptoms:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or lightheadedness
- Pain in the arms, neck, jaw, or back
Steps:
- Call emergency services immediately.
- Help the person stay calm and seated.
- Administer aspirin if advised.
- Perform CPR if they become unresponsive.
6. Dealing with Fractures and Sprains
Broken bones and sprains require careful handling to prevent further injury.
Steps:
- Immobilize the injured area – Do not attempt to realign the bone.
- Apply a cold compress – Reduces swelling and pain.
- Elevate the injury if possible.
- Seek medical attention immediately.
Being prepared for medical emergencies can make a significant difference in outcomes. Learning basic first aid skills ensures that you can provide effective assistance in critical situations. Regularly updating your knowledge and taking a certified first aid course can enhance your ability to respond confidently during emergencies.


