Edge computing is revolutionizing the way data is processed and analyzed. Unlike traditional cloud computing, which centralizes data processing in remote data centers, edge computing brings computation closer to the data source. This reduces latency, improves efficiency, and enhances security. As the demand for real-time data processing grows, edge computing is becoming an essential component of modern IT infrastructure.
1. What is Edge Computing?
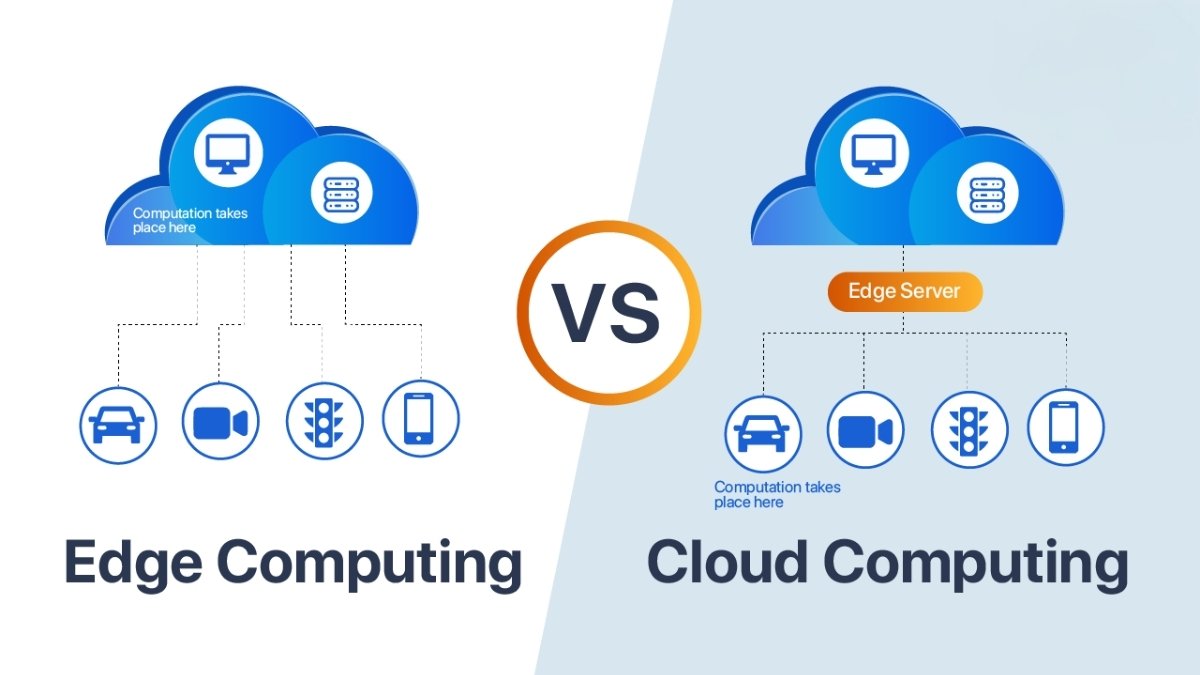
Edge computing refers to a distributed computing paradigm where data is processed near its source rather than relying on centralized cloud servers.
- Decentralized Processing: Data is analyzed and processed on local devices or edge servers.
- Reduced Latency: By minimizing the distance between data generation and processing, edge computing enables real-time decision-making.
- Enhanced Security: Sensitive data is processed closer to the source, reducing exposure to cyber threats.
2. Key Benefits of Edge Computing
Edge computing offers several advantages over traditional cloud computing:
- Faster Response Time: Processing data locally reduces the need to transmit large volumes of information to centralized servers, leading to quicker insights.
- Bandwidth Optimization: By reducing data transfer requirements, edge computing minimizes bandwidth usage and lowers operational costs.
- Scalability: Edge computing allows businesses to deploy computing power where it’s needed most, making it highly adaptable.
- Improved Reliability: Localized processing ensures that applications continue to function even if cloud connectivity is lost.

Read more: The Power of Microbiology: How Tiny Organisms Impact Our Lives
3. Applications of Edge Computing
Edge computing is transforming various industries by enabling faster and more efficient data processing.
a) Internet of Things (IoT)
- Smart home devices and industrial IoT systems use edge computing to process data in real time, reducing latency and improving automation.
- Examples: Smart thermostats, autonomous vehicles, and industrial sensors.
b) Healthcare
- Medical devices use edge computing to analyze patient data locally, ensuring rapid response times and reducing dependence on cloud servers.
- Examples: Remote patient monitoring and AI-driven diagnostics.
c) Retail and E-Commerce
- Retailers use edge computing for personalized customer experiences, inventory management, and fraud detection.
- Examples: AI-powered checkout systems and in-store analytics.
d) Autonomous Vehicles
- Self-driving cars rely on edge computing to process sensor data instantly for navigation and obstacle detection.
- Example: Tesla’s Autopilot system uses onboard computing power to make real-time driving decisions.
e) Smart Cities
- Edge computing helps manage traffic, energy consumption, and security in urban environments.
- Examples: Smart traffic lights and AI-based surveillance systems.
4. Challenges of Edge Computing
While edge computing offers significant advantages, it also comes with certain challenges:
- Infrastructure Costs: Setting up edge computing networks requires investment in hardware and software.
- Security Concerns: Distributing data processing across multiple locations increases the risk of cyber threats.
- Complex Deployment: Managing a distributed network of edge devices requires advanced IT expertise.
5. Future of Edge Computing
The adoption of edge computing is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. Key trends shaping its future include:
- AI-Powered Edge Computing: The integration of artificial intelligence at the edge will enable smarter, faster decision-making.
- 5G Connectivity: High-speed 5G networks will enhance edge computing by enabling ultra-low latency data transmission.
- Edge-as-a-Service (EaaS): Cloud providers are offering edge computing solutions as a service, simplifying deployment for businesses.
- Increased Security Measures: Advanced encryption and cybersecurity protocols will improve the safety of edge computing networks.
Conclusion
Edge computing is transforming modern data processing by enhancing speed, efficiency, and security. With its applications spanning industries like healthcare, retail, and smart cities, the role of edge computing will continue to expand. As technology advances, businesses must leverage edge computing to stay competitive in a data-driven world.