If you have these sings on the body see a doctor immediaely
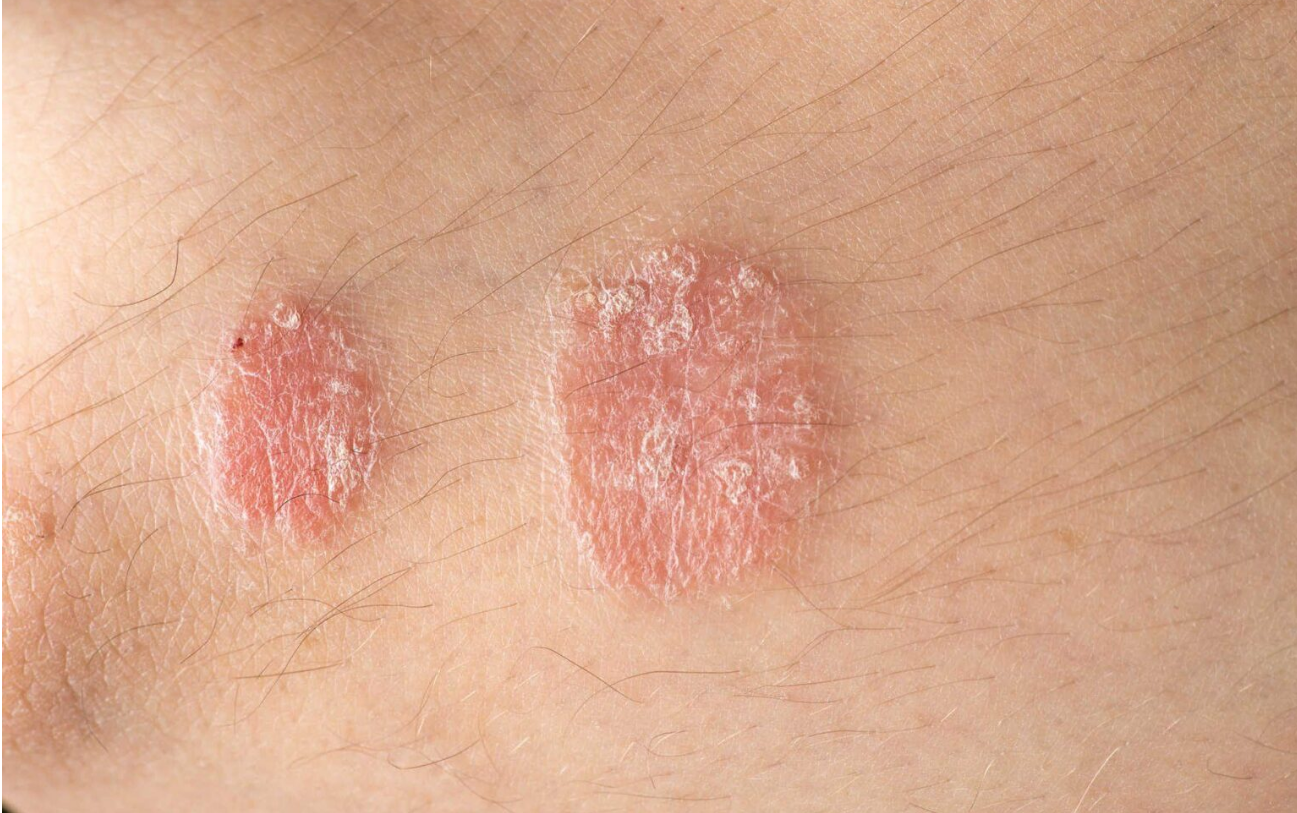
Psoriasis is a fairly common skin disease. People with psoriasis often experience itching, burning pain, discomfort, redness, and peeling skin. If psoriasis recurs many times, it can cause skin infections, arthritis, pustular psoriasis, erythema all over the body,…
1. Common types of psoriasis
1.1 Plaque psoriasis
This form of psoriasis causes red, inflamed areas of skin covered with silvery-white scales or plaques. The condition is most commonly found on the knees, elbows, and scalp.
1.2 Guttate psoriasis
Guttate psoriasiscauses small pink patches of skin. These are usually found on the trunk, arms, and legs. The patches are rarely as thick or raised as inplaque psoriasis.
1.3 Pustular psoriasis
Pustular psoriasisIt usually occurs in adults. It causes the skin to become inflamed and develop white pus-filled blisters. This form of psoriasis is usually limited to smaller areas of the skin, such as the hands or feet, but can spread.
1.4 Inverse psoriasis
This form of psoriasis causes shiny, red, inflamed patches of skin that develop in areas such as the armpits, breasts, groin, or around the skin folds of the genitals.
1.5 Erythrodermic psoriasis
This type of psoriasis causes the skin to look like it has been sunburned. The scaly patches often peel off in large patches. People with erythrodermic psoriasis are more likely to develop fevers and become seriously ill. This can be life-threatening, so see your doctor right away if you start to notice symptoms.
2. Is psoriasis contagious?
Psoriasis is a skin disease, so it cannot be passed from person to person. Touching a psoriasis lesion on a person’s body will not cause the person to get the disease.
3. What causes psoriasis?
3.1 Immune system
Autoimmune diseasesis the result of the body attacking itself. In the case of psoriasis, a type of white blood cell isT lymphocytesmistakenly attack skin cells.
In a normal human body, thewhite blood cellsdeployed to attack and destroy invading bacteria and combat infection.
In case ofpsoriasis, these cells have a mistake that causes the overproduction of skin cells. This causes new layers of skin cells to grow too quickly, being pushed to the surface of the skin and starting to pile up with other skin cells. The effects on skin cells also cause red, inflamed areas of skin to develop.
3.2 Genetic factors
If someone in your family has psoriasis, you’re more likely to develop the condition. Approximately 2 to 3 percent of people with psoriasis have a genetic predisposition to the condition, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF).
4. Factors that trigger psoriasis
The most common psoriasis triggers are:
4.1 Alcoholic beverages
AlcoholAlcoholic beverages containing high levels of alcohol can trigger psoriasis flare-ups. If you are consuming alcohol excessively, psoriasis flare-ups will occur more frequently.
4.2 Medicines
Certain medications are thought to trigger psoriasis. These include:
- Lithium
- Antimalarial drugs
- Blood pressure medication
4.3 Infection
If you are sick or fighting an infection, your immune system goes into overdrive fighting the infection. This makes it more likely that an outbreak will occur.Strep throatis also often a trigger for psoriasis.
5. Diagnosis of psoriasis
There are two tests or examinations needed to diagnose psoriasis.
5.1 Clinical examination
During this physical exam, show your doctor all the problem areas. Also, tell your doctor if anyone in your family has psoriasis.
5.2 Biopsy test
If symptoms are still unclear or the doctor wants to confirm their diagnosis, they may take a small sample of the patient’s skin tobiopsy.
6. Treatment options for psoriasis
There is no cure for psoriasis. Treatments typically aim to reduce inflammation and scaling, slow skin cell growth, and remove patches of psoriasis. Psoriasis treatments typically fall into three categories:
6.1 Topical treatment
Creams and ointments applied directly to the affected areas of skin can be very helpful in reducing the severity of mild to moderate psoriasis.
Topical medications used to treat psoriasis are:
- Topical corticosteroids
- Topical retinoids
- Anthralin drug
- Vitamin D and similar drugs
- Active ingredient salicylic acid
- Moisturizer
6.2 Immunosuppressive drugs
These drugs include:
- Methotrexate
- Sandimmune immunosuppressant
- Biological drugs
- Retinoid drugs
6.3 Phototherapy
This psoriasis treatment usesultraviolet (UV) rays or natural light. Sunlight helps destroy overactive white blood cells that damage skin cells and cause rapid skin cell growth. Both UVA and UVB rays can help relieve the symptoms of mild to moderate psoriasis.
For any questions that need to be answered by a specialist, as well as customers who need examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, please make an appointment on the website for good service.